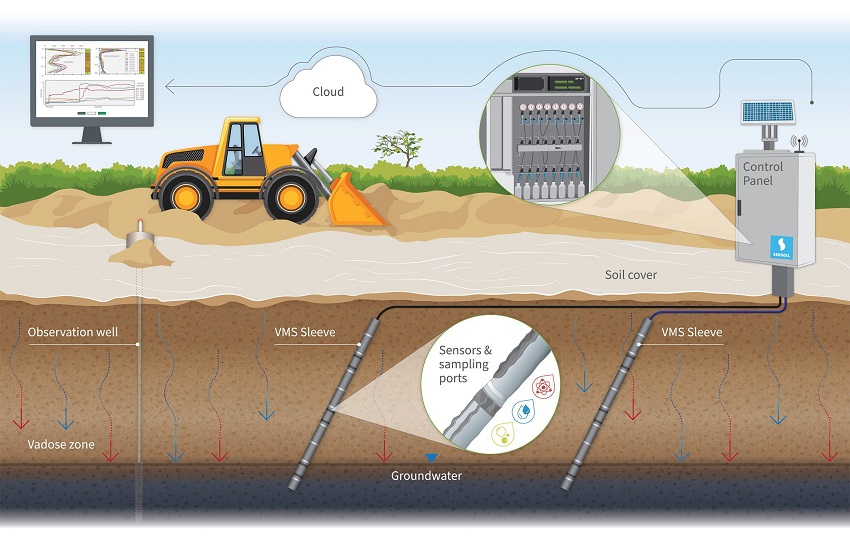
Contaminated sites pose a significant challenge to environmental health, public safety, and economic development. These sites, often resulting from industrial activities, improper waste disposal, or accidental spills, require effective remediation to restore them to a safe state. Chemical engineers play a vital role in this process, applying their expertise to develop and implement innovative solutions that address contamination issues. This article delves into the various responsibilities of chemical engineers in the remediation of contaminated sites, the technologies they utilize, and the methodologies they apply.
Understanding Contaminated Sites
Contaminated sites are areas where hazardous substances are present, potentially posing risks to human health and the environment. Common sources of contamination include:
- Industrial facilities (factories, refineries)
- Landfills and waste disposal sites
- Accidental spills (oil spills, chemical leaks)
- Mining operations
- Agricultural practices (pesticides, fertilizers)
The Importance of Remediation
The process of remediation involves cleaning up contaminated sites to mitigate risks and restore ecological health. Without remediation, these sites can lead to:
- Health hazards for nearby populations
- Environmental degradation
- Economic decline in affected areas
- Legal liabilities for responsible parties
Roles of Chemical Engineers in Remediation
Chemical engineers contribute to the remediation of contaminated sites through a variety of roles, including:
1. Site Assessment
Chemical engineers perform thorough site assessments to identify the type and extent of contamination. This often involves:
- Soil and groundwater sampling
- Analyzing chemical properties of contaminants
- Evaluating potential risks to human health and the environment
2. Selecting Remediation Technologies
Based on the assessment, chemical engineers determine the most appropriate remediation technologies. Common methods include:
- Bioremediation: Utilizing microorganisms to degrade contaminants.
- Phytoremediation: Using plants to absorb or degrade hazardous substances.
- Soil Washing: Physically removing contaminants from soil using water or chemical solvents.
- Thermal Desorption: Applying heat to volatilize and remove contaminants.
- Excavation: Physically removing contaminated soil or materials.
3. Designing Remediation Systems
Chemical engineers design remediation systems that are efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. This includes:
- Modeling the transport and fate of contaminants
- Designing treatment systems that can handle specific contaminants
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations
4. Implementation and Monitoring
Once a remediation plan is in place, chemical engineers oversee the implementation. Their responsibilities include:
- Coordinating fieldwork and remediation activities
- Monitoring the effectiveness of the remediation efforts
- Adjusting techniques based on real-time data and outcomes
Challenges Faced by Chemical Engineers
Despite their expertise, chemical engineers encounter several challenges during the remediation process, such as:
- Complexity of contamination scenarios
- Uncertainty in contaminant behavior
- Technical and financial constraints
- Regulatory and community engagement issues
Future Trends in Remediation
The field of remediation is continuously evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging. Future trends may include:
- Increased use of nanotechnology for targeted remediation
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for data analysis
- Enhanced bioremediation techniques using synthetic biology
- Greater emphasis on sustainable practices and green chemistry
Conclusion
Chemical engineers play an indispensable role in the remediation of contaminated sites, applying their knowledge and skills to protect public health and the environment. Through site assessments, technology selection, system design, and ongoing monitoring, they ensure that remediation efforts are effective and sustainable. As challenges continue to evolve, the contributions of chemical engineers will remain critical in developing innovative solutions to address contamination issues and restore contaminated lands.