Plastic, polymeric material that has the capability of being molded or shaped, usually by the application of heat and pressure. This property of plasticity, often found in combination with other special properties such as low density, low electrical conductivity, transparency, and toughness, allows plastics to be made into a great variety of products. These include tough and lightweight beverage bottles made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), flexible garden hoses made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), insulating food containers made of foamed polystyrene, and shatterproof windows made of polymethyl methacrylate.
In this article a brief review of the essential properties of plastics is provided, followed by a more detailed description of their processing into useful products and subsequent recycling. For a fuller understanding of the materials from which plastics are made, see chemistry of industrial polymers.
The Composition, Structure, And Properties Of Plastics
Many of the chemical names of the polymers employed as plastics have become familiar to consumers, although some are better known by their abbreviations or trade names. Thus, polyethylene terephthalate and polyvinyl chloride are commonly referred to as PET and PVC, while foamed polystyrene and polymethyl methacrylate are known by their trademarked names, Styrofoam and Plexiglas (or Perspex).
Industrial fabricators of plastic products tend to think of plastics as either “commodity” resins or “specialty” resins. (The term resin dates from the early years of the plastics industry; it originally referred to naturally occurring amorphous solids such as shellac and rosin.) Commodity resins are plastics that are produced at high volume and low cost for the most common disposable items and durable goods. They are represented chiefly by polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene. Specialty resins are plastics whose properties are tailored to specific applications and that are produced at low volume and higher cost. Among this group are the so-called engineering plastics, or engineering resins, which are plastics that can compete with die-cast metals in plumbing, hardware, and automotive applications. Important engineering plastics, less familiar to consumers than the commodity plastics listed above, are polyacetal, polyamide (particularly those known by the trade name nylon), polytetrafluoroethylene (trademark Teflon), polycarbonate, polyphenylene sulfide, epoxy, and polyetheretherketone. Another member of the specialty resins is thermoplastic elastomers, polymers that have the elastic properties of rubber yet can be molded repeatedly upon heating. Thermoplastic elastomers are described in the article elastomer.
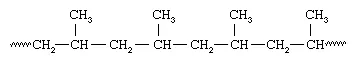
Plastics also can be divided into two distinct categories on the basis of their chemical composition. One category is plastics that are made up of polymers having only aliphatic (linear) carbon atoms in their backbone chains. All the commodity plastics listed above fall into this category. The structure of polypropylene can serve as an example; here attached to every other carbon atom is a pendant methyl group (CH3):

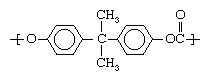
The other category of plastics is made up of heterochain polymers. These compounds contain atoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur in their backbone chains, in addition to carbon. Most of the engineering plastics listed above are composed of heterochain polymers. An example would be polycarbonate, whose molecules contain two aromatic (benzene) rings:
The distinction between carbon-chain and heterochain polymers is reflected in the table, in which selected properties and applications of the most important carbon-chain and heterochain plastics are shown and from which links are provided directly to entries that describe these materials in greater detail. It is important to note that for each polymer type listed in the table there can be many subtypes, since any of a dozen industrial producers of any polymer can offer 20 or 30 different variations for use in specific applications. For this reason the properties indicated in the table must be taken as approximations.
Properties and applications of commercially important plastics
| *All values shown are for glass-fibre-reinforced samples (except for polyurethane). | |||||
| polymer family and type | density (g/cm3) | degree of crystallinity | glass transition temperature (°C) | crystal melting temperature (°C) | deflection temperature at 1.8 MPa (°C) |
| Thermoplastics | |||||
| Carbon-chain | |||||
| high-density polyethylene (HDPE) | 0.95–0.97 | high | –120 | 137 | — |
| low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | 0.92–0.93 | moderate | −120 | 110 | — |
| polypropylene (PP) | 0.90–0.91 | high | −20 | 176 | — |
| polystyrene (PS) | 1.0–1.1 | nil | 100 | — | — |
| acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) | 1.0–1.1 | nil | 90–120 | — | — |
| polyvinyl chloride, unplasticized (PVC) | 1.3–1.6 | nil | 85 | — | — |
| polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) | 1.2 | nil | 115 | — | — |
| polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | 2.1–2.2 | moderate-high | 126 | 327 | — |
| Heterochain | |||||
| polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 1.3–1.4 | moderate | 69 | 265 | — |
| polycarbonate (PC) | 1.2 | low | 145 | 230 | — |
| polyacetal | 1.4 | moderate | –50 | 180 | — |
| polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | 1.3 | nil | 185 | — | — |
| polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) | 1.35 | moderate | 88 | 288 | — |
| cellulose diacetate | 1.3 | low | 120 | 230 | — |
| polycaprolactam (nylon 6) | 1.1–1.2 | moderate | 50 | 210–220 | — |
| Thermosets* | |||||
| Heterochain | |||||
| polyester (unsaturated) | 1.3–2.3 | nil | — | — | 200 |
| epoxies | 1.1–1.4 | nil | — | — | 110–250 |
| phenol formaldehyde | 1.7–2.0 | nil | — | — | 175–300 |
| urea and melamine formaldehyde | 1.5–2.0 | nil | — | — | 190–200 |
| polyurethane | 1.05 | low | — | — | 90–100 |
| polymer family and type | tensile strength (MPa) | elongation at break (%) | flexural modulus (GPa) | typical products and applications | |
| Thermoplastics | |||||
| Carbon-chain | |||||
| high-density polyethylene (HDPE) | 20–30 | 10–1,000 | 1–1.5 | milk bottles, wire and cable insulation, toys | |
| low-density polyethylene (LDPE) | 8–30 | 100–650 | 0.25–0.35 | packaging film, grocery bags, agricultural mulch | |
| polypropylene (PP) | 30–40 | 100–600 | 1.2–1.7 | bottles, food containers, toys | |
| polystyrene (PS) | 35–50 | 1–2 | 2.6–3.4 | eating utensils, foamed food containers | |
| acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) | 15–55 | 30–100 | 0.9–3.0 | appliance housings, helmets, pipe fittings | |
| polyvinyl chloride, unplasticized (PVC) | 40–50 | 2–80 | 2.1–3.4 | pipe, conduit, home siding, window frames | |
| polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) | 50–75 | 2–10 | 2.2–3.2 | impact-resistant windows, skylights, canopies | |
| polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | 20–35 | 200–400 | 0.5 | self-lubricated bearings, nonstick cookware | |
| Heterochain | |||||
| polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 50–75 | 50–300 | 2.4–3.1 | transparent bottles, recording tape | |
| polycarbonate (PC) | 65–75 | 110–120 | 2.3–2.4 | compact discs, safety glasses, sporting goods | |
| polyacetal | 70 | 25–75 | 2.6–3.4 | bearings, gears, shower heads, zippers | |
| polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | 70–105 | 30–150 | 3.9 | machine, automotive, and aerospace parts | |
| polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) | 50–90 | 1–10 | 3.8–4.5 | machine parts, appliances, electrical equipment | |
| cellulose diacetate | 15–65 | 6–70 | 1.5 | photographic film | |
| polycaprolactam (nylon 6) | 40–170 | 30–300 | 1.0–2.8 | bearings, pulleys, gears | |
| Thermosets* | |||||
| Heterochain | |||||
| polyester (unsaturated) | 20–70 | <3 | 7–14 | boat hulls, automobile panels | |
| epoxies | 35–140 | <4 | 14–30 | laminated circuit boards, flooring, aircraft parts | |
| phenol formaldehyde | 50–125 | <1 | 8–23 | electrical connectors, appliance handles | |
| urea and melamine formaldehyde | 35–75 | <1 | 7.5 | countertops, dinnerware | |
| polyurethane | 70 | 3–6 | 4 | flexible and rigid foams for upholstery |


