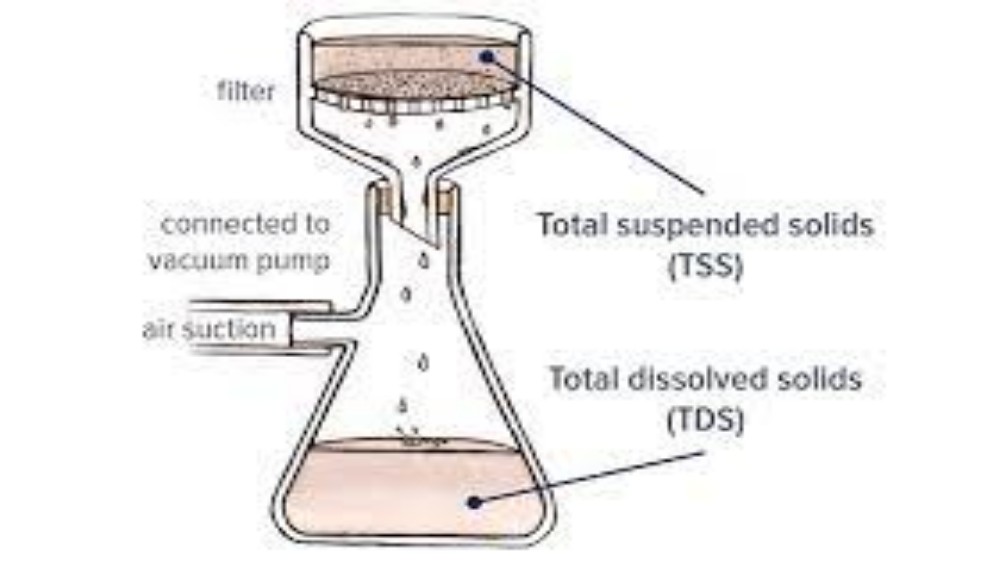
Total dissolved solids as reported on an analysis are the total of all minerals dissolved in the water. TDS levels below 900 ppm do not present a problem in residential or commercial applications. TDS levels above 900 ppm will affect the performance of water softeners in the form of hardness and iron “leakage”. All waters contain some natural sodium, and the higher the TDS, usually the higher the sodium level.
Sodium is used to regenerate a water softener and high levels of natural occurring sodium, plus that used to remove the hardness, will combine to a level high enough to partially regenerate the softener. Thus, water with a TDS of 1500 ppm and 40 grains of hardness will cause hardness and iron leakage.
TDS is also a factor in performance of Reverse Osmosis Systems. The R.O. membrane has limitations on TDS due to its ability or inability to carry away solids which might plug the membrane.